Introduction
On this page
Introduction#
Continuously tested on Linux, MacOS and Windows:
New 2021 paper:
OpenPifPaf: Composite Fields for Semantic Keypoint Detection and Spatio-Temporal Association
Sven Kreiss, Lorenzo Bertoni, Alexandre Alahi, 2021.Many image-based perception tasks can be formulated as detecting, associating and tracking semantic keypoints, e.g., human body pose estimation and tracking. In this work, we present a general framework that jointly detects and forms spatio-temporal keypoint associations in a single stage, making this the first real-time pose detection and tracking algorithm. We present a generic neural network architecture that uses Composite Fields to detect and construct a spatio-temporal pose which is a single, connected graph whose nodes are the semantic keypoints (e.g., a person’s body joints) in multiple frames. For the temporal associations, we introduce the Temporal Composite Association Field (TCAF) which requires an extended network architecture and training method beyond previous Composite Fields. Our experiments show competitive accuracy while being an order of magnitude faster on multiple publicly available datasets such as COCO, CrowdPose and the PoseTrack 2017 and 2018 datasets. We also show that our method generalizes to any class of semantic keypoints such as car and animal parts to provide a holistic perception framework that is well suited for urban mobility such as self-driving cars and delivery robots.
Previous CVPR 2019 paper.
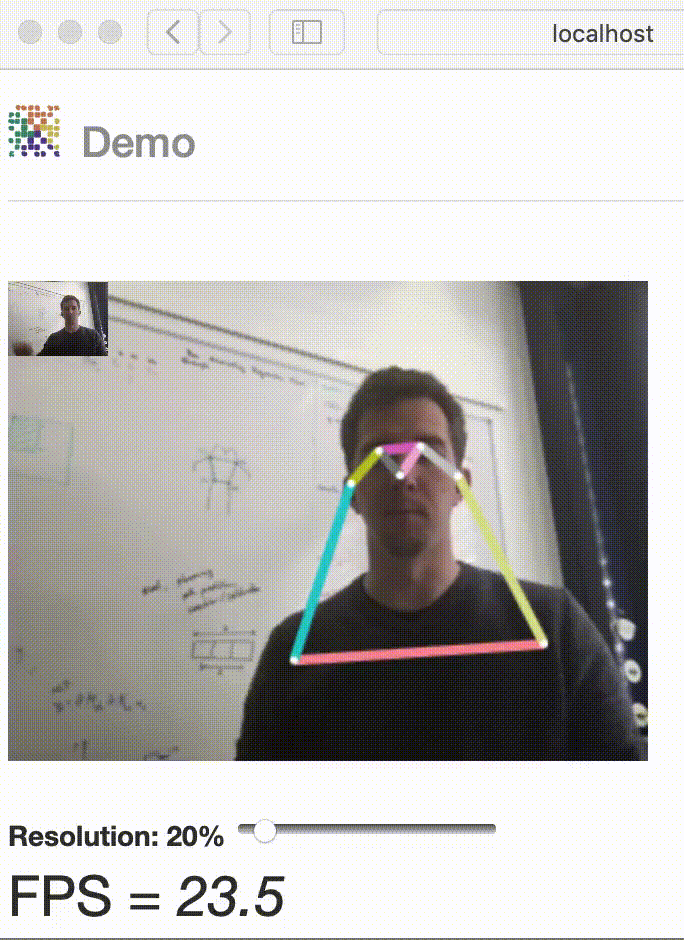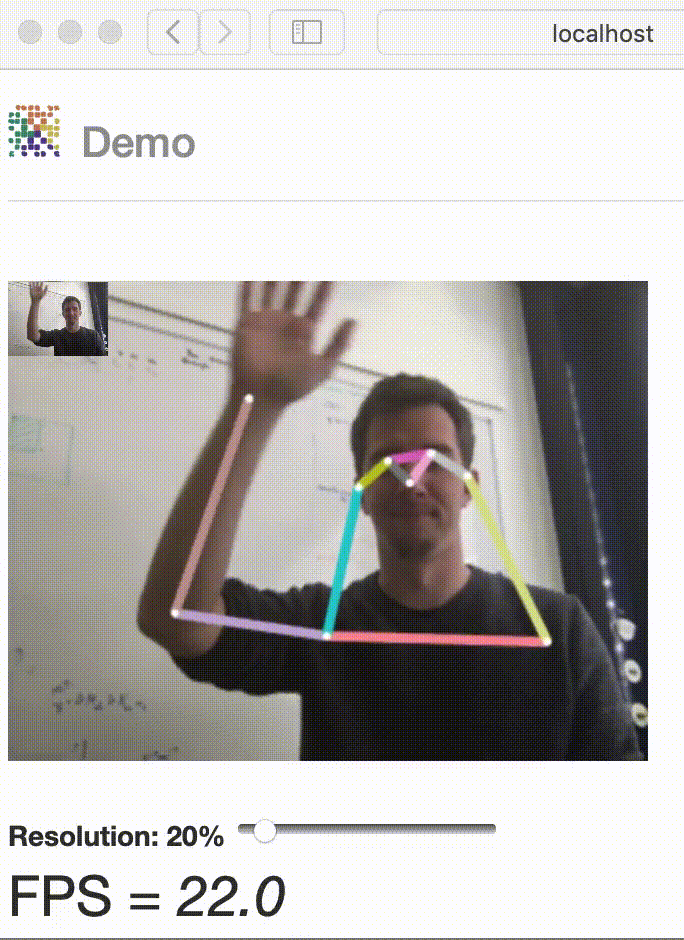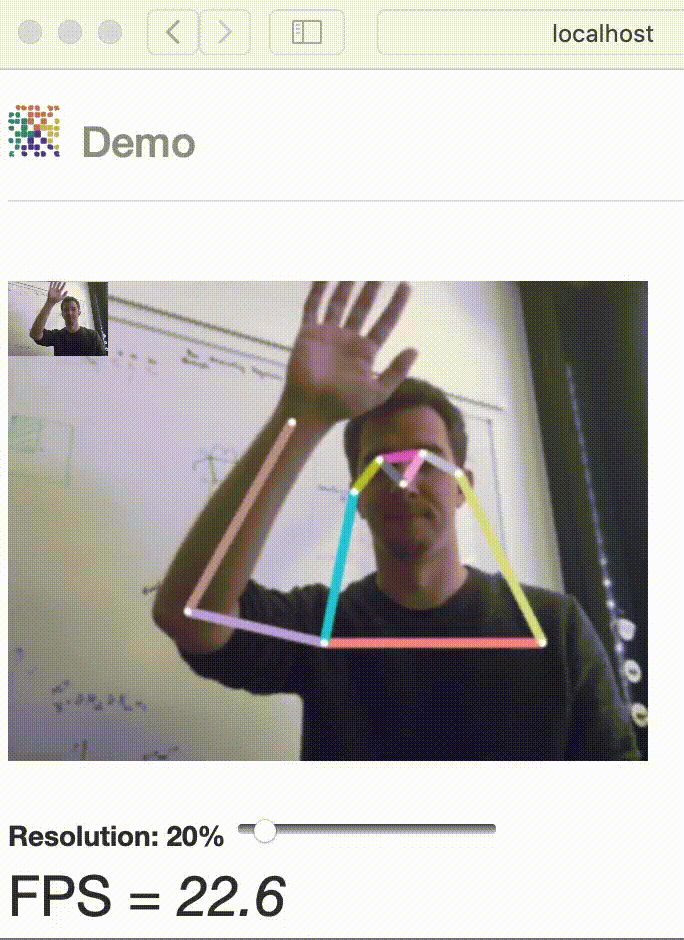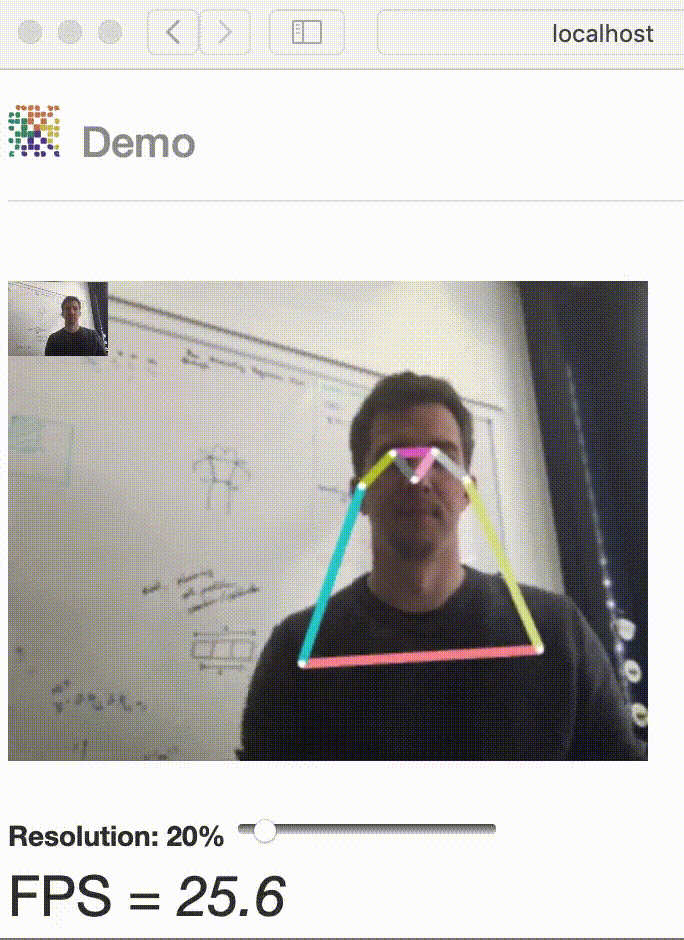
Have fun with our latest real-time interactive demo!
Demo#
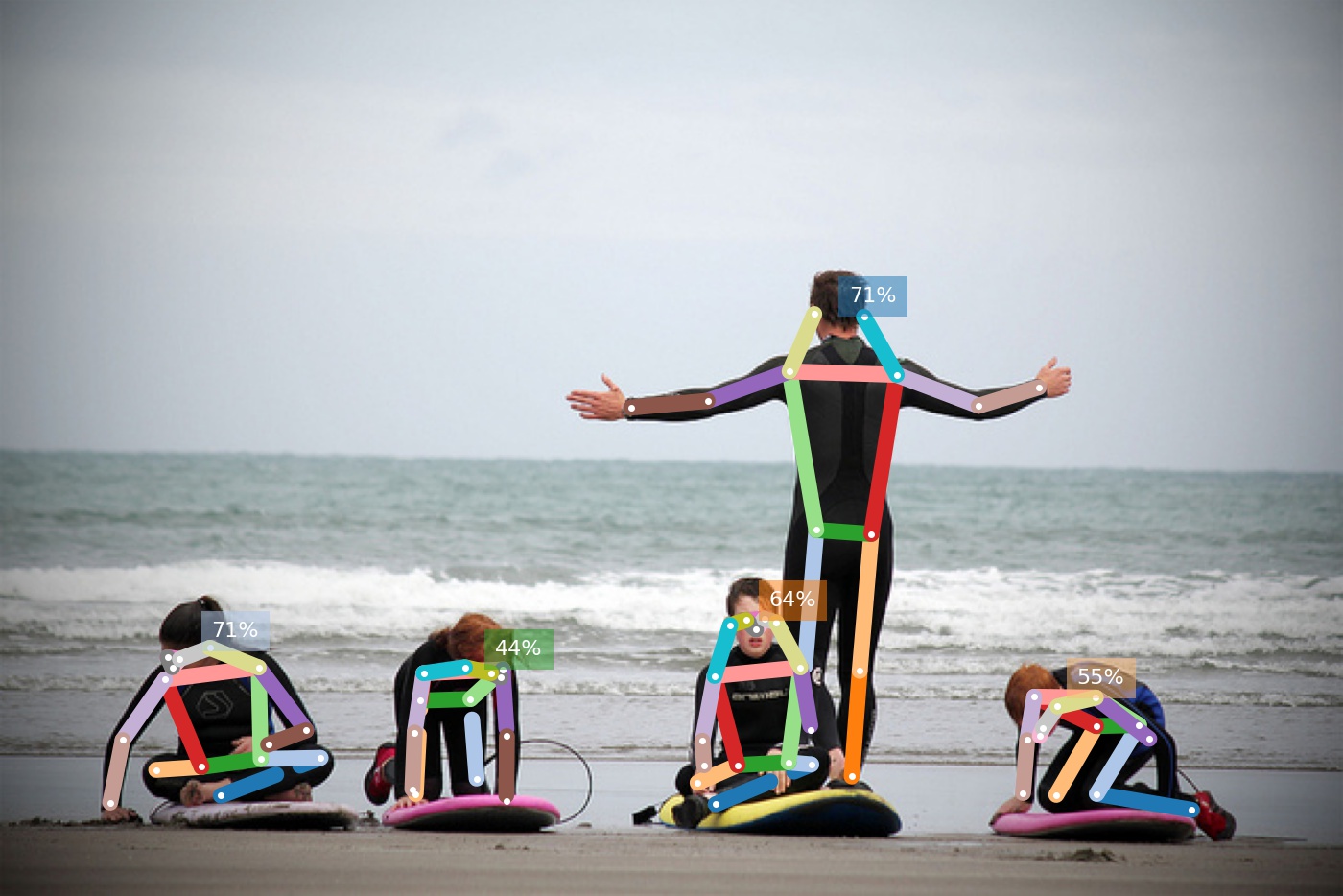

Image credit: “Learning to surf” by fotologic which is licensed under CC-BY-2.0.
Created with:
python3 -m openpifpaf.predict docs/coco/000000081988.jpg --image-output
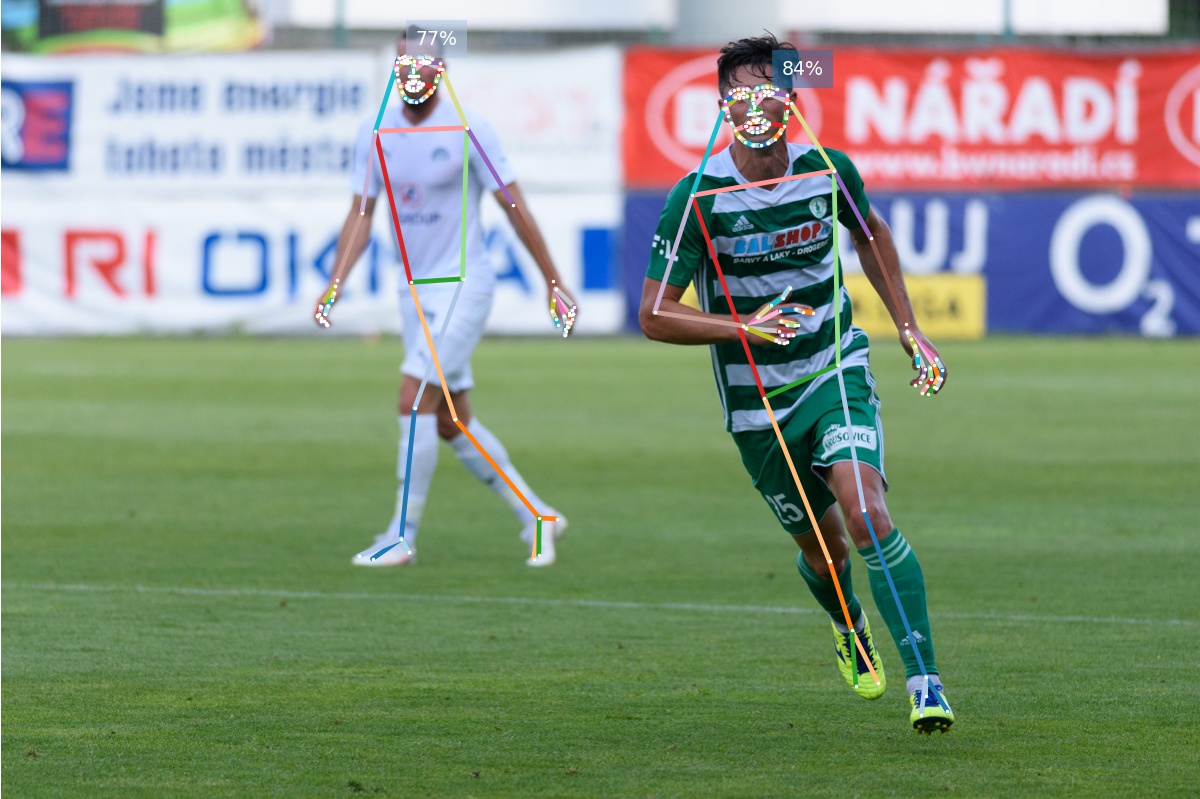 Image credit: Photo by Lokomotive74 which is licensed under CC-BY-4.0.
Image credit: Photo by Lokomotive74 which is licensed under CC-BY-4.0.
Created with:
python3 -m openpifpaf.predict docs/wholebody/soccer.jpeg --checkpoint=shufflenetv2k30-wholebody --line-width=2 --image-output
More demos:
openpifpafwebdemo project (best performance). Live.
OpenPifPaf running in your browser: openpifpaf.github.io/openpifpafwebdemo (experimental)
the python3 -m openpifpaf.video command (requires OpenCV)
Install#
This version of OpenPifPaf (openpifpaf-vita) cannot co-exist with the original one (openpifpaf) in the same environment.
If you have previously installed the package openpifpaf, remove it before installation to avoid conflicts.
This project was forked from OpenPifPaf v0.13.1 and developed separately from version v0.14.0 on.
Do not clone this repository.
Make sure there is no folder named openpifpaf-vita in your current directory, and run:
pip3 install openpifpaf-vita
You need to install matplotlib to produce visual outputs:
pip3 install matplotlib
To modify OpenPifPaf itself, please follow Modify Code.
For a live demo, we recommend to try the openpifpafwebdemo project. Alternatively, python3 -m openpifpaf.video (requires OpenCV) provides a live demo as well.
Pre-trained Models#
Performance metrics on the COCO val set obtained with a GTX1080Ti:
Name |
AP |
AP0.5 |
AP0.75 |
APM |
APL |
t_{total} [ms] |
t_{NN} [ms] |
t_{dec} [ms] |
size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
47.1 |
73.9 |
49.5 |
40.1 |
58.0 |
26 |
9 |
14 |
5.8MB |
|
58.4 |
82.3 |
63.4 |
52.3 |
67.9 |
34 |
19 |
12 |
15.0MB |
|
68.1 |
87.8 |
74.4 |
65.4 |
73.0 |
53 |
38 |
12 |
97.4MB |
|
68.1 |
87.6 |
74.5 |
63.0 |
76.0 |
40 |
28 |
10 |
38.9MB |
|
71.8 |
89.4 |
78.1 |
67.0 |
79.5 |
81 |
71 |
8 |
115.0MB |
Command to reproduce this table: python -m openpifpaf.benchmark –checkpoints resnet50 shufflenetv2k16 shufflenetv2k30.
Performance metrics on the COCO val set obtained with a NVIDIA A100:
Name |
AP |
AP0.5 |
AP0.75 |
APM |
APL |
t_{total} [ms] |
t_{NN} [ms] |
t_{dec} [ms] |
size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
69.3 |
87.8 |
75.5 |
63.2 |
78.4 |
110 |
86 |
15 |
688MB |
|
70.5 |
87.9 |
76.9 |
64.2 |
79.7 |
138 |
113 |
17 |
338MB |
|
73.4 |
89.9 |
80.0 |
69.1 |
80.2 |
312 |
239 |
62 |
331MB |
|
73.8 |
90.1 |
80.2 |
69.7 |
80.4 |
112 |
73 |
30 |
115MB |
|
75.8 |
90.9 |
82.6 |
72.1 |
81.8 |
635 |
606 |
23 |
750MB |
Pretrained model files are shared in the vita-epfl/openpifpaf-torchhub and openpifpaf/torchhub
repositories and linked from the checkpoint names in the table above.
The pretrained models are downloaded automatically when
using the command line option --checkpoint checkpointasintableabove.
Executable Guide#
This is a jupyter-book or “executable book”. Many sections of this book, like Prediction, are generated from the code shown on the page itself: most pages are based on Jupyter Notebooks that can be downloaded or launched interactively in the cloud by clicking on the rocket at the top and selecting a cloud provider like Binder. The code on the page is all the code required to reproduce that particular page.
Citation#
Reference [KBA21], arxiv.org/abs/2103.02440
@article{kreiss2021openpifpaf,
title = {{OpenPifPaf: Composite Fields for Semantic Keypoint Detection and Spatio-Temporal Association}},
author = {Sven Kreiss and Lorenzo Bertoni and Alexandre Alahi},
journal = {IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems},
pages = {1-14},
month = {March},
year = {2021}
}
Reference [KBA19], arxiv.org/abs/1903.06593
@InProceedings{kreiss2019pifpaf,
author = {Kreiss, Sven and Bertoni, Lorenzo and Alahi, Alexandre},
title = {{PifPaf: Composite Fields for Human Pose Estimation}},
booktitle = {The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2019}
}
Commercial License#
This software is available for licensing via the EPFL Technology Transfer Office (https://tto.epfl.ch/, info.tto@epfl.ch).